Difference between revisions of "SacC"
(→References) |
|||
| Line 122: | Line 122: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | + | ==Reviews== | |
| + | <pubmed>20735481 </pubmed> | ||
| + | ==Original publications== | ||
<pubmed>3112519 2117666, 19635162 1900939 1924373 7592486</pubmed> | <pubmed>3112519 2117666, 19635162 1900939 1924373 7592486</pubmed> | ||
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 12:34, 26 August 2010
- Description: levanase
| Gene name | sacC |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | levanase |
| Function | degradation of levan to fructose |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Sugar catabolism | |
| MW, pI | 75 kDa, 6.789 |
| Gene length, protein length | 2031 bp, 677 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yraA, levG |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 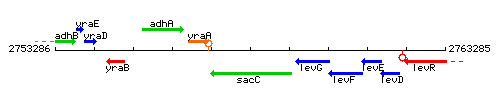
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU27030
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Hydrolysis of terminal, non-reducing (2->1)- and (2->6)-linked beta-D-fructofuranose residues in fructans (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: glycosyl hydrolase 32 family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P05656
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 3.2.1.80
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
Maria Elena Ortiz-Soto, Enrique Rudiño-Piñera, Maria Elena Rodriguez-Alegria, Agustin Lopez Munguia
Evaluation of cross-linked aggregates from purified Bacillus subtilis levansucrase mutants for transfructosylation reactions.
BMC Biotechnol: 2009, 9;68
[PubMed:19635162]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
I Martin-Verstraete, J Stülke, A Klier, G Rapoport
Two different mechanisms mediate catabolite repression of the Bacillus subtilis levanase operon.
J Bacteriol: 1995, 177(23);6919-27
[PubMed:7592486]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Débarbouillé, I Martin-Verstraete, F Kunst, G Rapoport
The Bacillus subtilis sigL gene encodes an equivalent of sigma 54 from gram-negative bacteria.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1991, 88(20);9092-6
[PubMed:1924373]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Débarbouillé, I Martin-Verstraete, A Klier, G Rapoport
The transcriptional regulator LevR of Bacillus subtilis has domains homologous to both sigma 54- and phosphotransferase system-dependent regulators.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1991, 88(6);2212-6
[PubMed:1900939]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
I Martin-Verstraete, M Débarbouillé, A Klier, G Rapoport
Levanase operon of Bacillus subtilis includes a fructose-specific phosphotransferase system regulating the expression of the operon.
J Mol Biol: 1990, 214(3);657-71
[PubMed:2117666]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
I Martin, M Débarbouillé, E Ferrari, A Klier, G Rapoport
Characterization of the levanase gene of Bacillus subtilis which shows homology to yeast invertase.
Mol Gen Genet: 1987, 208(1-2);177-84
[PubMed:3112519]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)