Difference between revisions of "XylB"
(→Expression and regulation) |
|||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| − | * '''Structure:''' | + | * '''Structure:''' [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/cgi/explore.cgi?pdbId=2NLX 2NLX] (from ''E. coli'', 35% identity, 52% similarity) {{PubMed|17123542}} |
* '''UniProt:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P39211 P39211] | * '''UniProt:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P39211 P39211] | ||
| Line 125: | Line 125: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | + | <pubmed>17123542 1921970 2454911 8132469</pubmed> | |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 10:00, 18 February 2010
- Description: xylulokinase
| Gene name | xylB |
| Synonyms | yncA |
| Essential | no |
| Product | xylulokinase |
| Function | utilization of xylan and xylose |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Sugar catabolism | |
| MW, pI | 55 kDa, 6.459 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1497 bp, 499 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | xylA, yncB |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 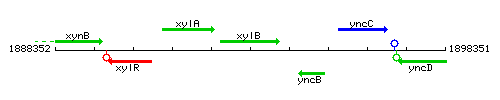
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU17610
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP + D-xylulose = ADP + D-xylulose 5-phosphate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: FGGY kinase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- UniProt: P39211
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.7.1.17
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Wolfgang Hillen, Erlangen University, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References