Difference between revisions of "PGP172"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
[[File:PGP172_cloning_region.jpeg|250px|thumb|right|'''pGP172 cloning region: click to enlarge''']] | [[File:PGP172_cloning_region.jpeg|250px|thumb|right|'''pGP172 cloning region: click to enlarge''']] | ||
| − | |||
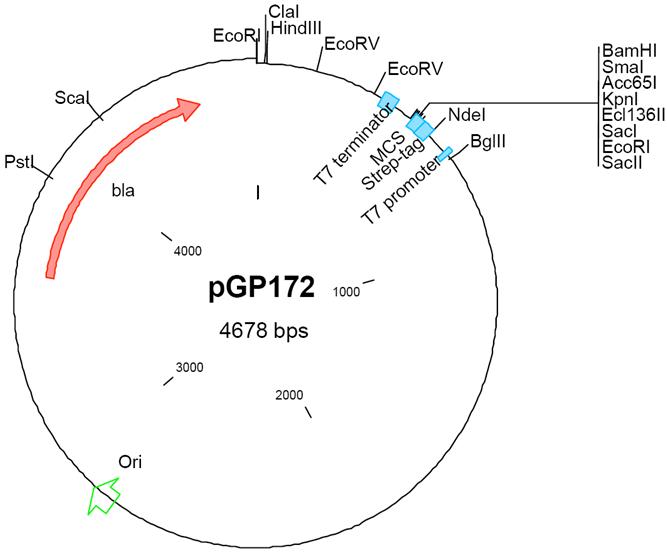
vector for the expression of proteins in E. coli, the plasmid allows to fuse a Strep-tag to the N-terminus of the expressed protein | vector for the expression of proteins in E. coli, the plasmid allows to fuse a Strep-tag to the N-terminus of the expressed protein | ||
Revision as of 11:33, 16 April 2009
vector for the expression of proteins in E. coli, the plasmid allows to fuse a Strep-tag to the N-terminus of the expressed protein
host: E. coli BL21(DE3)/pLysS, expression of the desired protein is induced by the addition of 1 mM IPTG to the culture
constructed in the Stülke lab
in E. coli: ampicillin resistance
based on pET3C
similar plasmid: pGP574
sequencing primer:
- CD13: 5’-AAACATATGGCTAGCTGGAGCCACCCGCAGTTC -3’
- NP20: 5’-GCAGCAGCCAACTCAGCTTCCTTTCGGGC-3’
Merzbacher, M., Detsch, C., Hillen, W. & Stülke, J. (2004) Mycoplasma pneumoniae HPr kinase/ phosphorylase: Assigning functional roles to the P-loop and HPr kinase/ phosphorylase signature sequence motif. Eur. J. Biochem. 271: 367-374. PubMed