Difference between revisions of "Hag"
(→References) |
|||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ||
| − | + | * no swarming motility on B medium. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/19202088 PubMed] | |
| + | * not essential for pellicle biofilm formation, but mutant is outcompeted by the wild-type strain when competed during pellicle formation {{PubMed|26122431}} | ||
| + | * few hours delay in pellicle development {{PubMed|26122431}} | ||
| + | * mutant has increased fitness in planktonic culture when competed with the wild-type NCIB3610 strain {{PubMed|26122431}} | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| Line 145: | Line 148: | ||
** 1A783 ( ''hag''::''erm''), {{PubMed|2174860}}, available at [http://pasture.asc.ohio-state.edu/BGSC/getdetail.cfm?bgscid=1A783&Search=1A783 BGSC] | ** 1A783 ( ''hag''::''erm''), {{PubMed|2174860}}, available at [http://pasture.asc.ohio-state.edu/BGSC/getdetail.cfm?bgscid=1A783&Search=1A783 BGSC] | ||
** 1A842 ( ''hag''::''kan''), {{PubMed|14762011}}, available at [http://pasture.asc.ohio-state.edu/BGSC/getdetail.cfm?bgscid=1A842&Search=1A842 BGSC] | ** 1A842 ( ''hag''::''kan''), {{PubMed|14762011}}, available at [http://pasture.asc.ohio-state.edu/BGSC/getdetail.cfm?bgscid=1A842&Search=1A842 BGSC] | ||
| + | ** DS1677 (marker-less in NCIB3610) {{PubMed|18566286}} | ||
| + | ** TB191 ''amyE''::Phy-''sfgfp'' (marker-less in NCIB3610 with constitutive expressed ''sfgfp'') {{PubMed|26122431}} | ||
| + | ** TB207 ''amyE''::Phy-''mKATE2'' (marker-less in NCIB3610 with constitutive expressed ''mKATE2'') {{PubMed|26122431}} | ||
| + | |||
* '''Expression vector:''' | * '''Expression vector:''' | ||
| Line 158: | Line 165: | ||
=Labs working on this gene/protein= | =Labs working on this gene/protein= | ||
| + | * [[Daniel Kearns]] | ||
=Your additional remarks= | =Your additional remarks= | ||
| Line 165: | Line 173: | ||
<pubmed>22672726 25251856 </pubmed> | <pubmed>22672726 25251856 </pubmed> | ||
==Original Publications== | ==Original Publications== | ||
| − | <pubmed> 23144244 21602220 21856853 2498284,9648743,9096206,7708689,19202088, 18763711, 21895793 10809682 19118355 17555441 20534509 15378759</pubmed> | + | <pubmed> 18566286,26122431,23144244 21602220 21856853 2498284,9648743,9096206,7708689,19202088, 18763711, 21895793 10809682 19118355 17555441 20534509 15378759</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 13:08, 2 July 2015
- Description: flagellin protein, about 20,000 subunits make up one flagellum
| Gene name | hag |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | flagellin protein |
| Function | motility and chemotaxis |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: hag | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: Hag | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Hag | |
| MW, pI | 32 kDa, 4.782 |
| Gene length, protein length | 912 bp, 304 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yvyC, csrA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 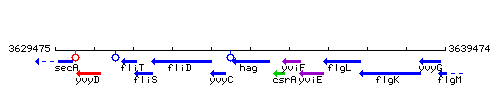
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
motility and chemotaxis, most abundant proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
CodY regulon, CsrA regulon, ScoC regulon, SigD regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU35360
Phenotypes of a mutant
- no swarming motility on B medium. PubMed
- not essential for pellicle biofilm formation, but mutant is outcompeted by the wild-type strain when competed during pellicle formation PubMed
- few hours delay in pellicle development PubMed
- mutant has increased fitness in planktonic culture when competed with the wild-type NCIB3610 strain PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU35360
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: bacterial flagellin family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): YvzB (C-terminal domain of Hag)
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU35360
- Structure: 3A5X (from Salmonella typhimurium, 42% identity)
- UniProt: P02968
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- the hag gene is strongly overexpressed in a ymdB mutant (loss of bistable gene expression) PubMed
- belongs to the 100 most abundant proteins PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 150241 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 280953 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 9552 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 11147 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 24114 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP901 (aphA3), GP902 (tet) PubMed, both available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- 1A915 ( hag::cat), PubMed, available at BGSC
- 1A783 ( hag::erm), PubMed, available at BGSC
- 1A842 ( hag::kan), PubMed, available at BGSC
- DS1677 (marker-less in NCIB3610) PubMed
- TB191 amyE::Phy-sfgfp (marker-less in NCIB3610 with constitutive expressed sfgfp) PubMed
- TB207 amyE::Phy-mKATE2 (marker-less in NCIB3610 with constitutive expressed mKATE2) PubMed
- Expression vector:
- expression in B. subtilis, in pBQ200: pGP1089, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- lacZ fusion: pGP1035 (in pAC6), pGP755 (in pAC7), there is also a series of promoter deletion variants in pAC6 and pAC7 PubMed, all available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- GFP fusion: BP494 (bglS:: (hag-promoter-cfp-aphA3)), BP496 (amyE:: (hag-promoter-iyfp-cat)), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Sampriti Mukherjee, Daniel B Kearns
The structure and regulation of flagella in Bacillus subtilis.
Annu Rev Genet: 2014, 48;319-40
[PubMed:25251856]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Tony Romeo, Christopher A Vakulskas, Paul Babitzke
Post-transcriptional regulation on a global scale: form and function of Csr/Rsm systems.
Environ Microbiol: 2013, 15(2);313-24
[PubMed:22672726]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Original Publications
Theresa Hölscher, Benjamin Bartels, Yu-Cheng Lin, Ramses Gallegos-Monterrosa, Alexa Price-Whelan, Roberto Kolter, Lars E P Dietrich, Ákos T Kovács
Motility, Chemotaxis and Aerotaxis Contribute to Competitiveness during Bacterial Pellicle Biofilm Development.
J Mol Biol: 2015, 427(23);3695-3708
[PubMed:26122431]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Sampriti Mukherjee, Paul Babitzke, Daniel B Kearns
FliW and FliS function independently to control cytoplasmic flagellin levels in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2013, 195(2);297-306
[PubMed:23144244]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Sampriti Mukherjee, Helen Yakhnin, Dave Kysela, Josh Sokoloski, Paul Babitzke, Daniel B Kearns
CsrA-FliW interaction governs flagellin homeostasis and a checkpoint on flagellar morphogenesis in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2011, 82(2);447-61
[PubMed:21895793]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Christine Diethmaier, Nico Pietack, Katrin Gunka, Christoph Wrede, Martin Lehnik-Habrink, Christina Herzberg, Sebastian Hübner, Jörg Stülke
A novel factor controlling bistability in Bacillus subtilis: the YmdB protein affects flagellin expression and biofilm formation.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(21);5997-6007
[PubMed:21856853]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kassem Hamze, Sabine Autret, Krzysztof Hinc, Soumaya Laalami, Daria Julkowska, Romain Briandet, Margareth Renault, Cédric Absalon, I Barry Holland, Harald Putzer, Simone J Séror
Single-cell analysis in situ in a Bacillus subtilis swarming community identifies distinct spatially separated subpopulations differentially expressing hag (flagellin), including specialized swarmers.
Microbiology (Reading): 2011, 157(Pt 9);2456-2469
[PubMed:21602220]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Gert Bange, Nico Kümmerer, Christoph Engel, Gunes Bozkurt, Klemens Wild, Irmgard Sinning
FlhA provides the adaptor for coordinated delivery of late flagella building blocks to the type III secretion system.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2010, 107(25);11295-300
[PubMed:20534509]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kassem Hamze, Daria Julkowska, Sabine Autret, Krzysztof Hinc, Krzysztofa Nagorska, Agnieszka Sekowska, I Barry Holland, Simone J Séror
Identification of genes required for different stages of dendritic swarming in Bacillus subtilis, with a novel role for phrC.
Microbiology (Reading): 2009, 155(Pt 2);398-412
[PubMed:19202088]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Prashant Kodgire, K Krishnamurthy Rao
hag expression in Bacillus subtilis is both negatively and positively regulated by ScoC.
Microbiology (Reading): 2009, 155(Pt 1);142-149
[PubMed:19118355]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hannes Hahne, Susanne Wolff, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
From complementarity to comprehensiveness--targeting the membrane proteome of growing Bacillus subtilis by divergent approaches.
Proteomics: 2008, 8(19);4123-36
[PubMed:18763711]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kris M Blair, Linda Turner, Jared T Winkelman, Howard C Berg, Daniel B Kearns
A molecular clutch disables flagella in the Bacillus subtilis biofilm.
Science: 2008, 320(5883);1636-8
[PubMed:18566286]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Helen Yakhnin, Pallavi Pandit, Tom J Petty, Carol S Baker, Tony Romeo, Paul Babitzke
CsrA of Bacillus subtilis regulates translation initiation of the gene encoding the flagellin protein (hag) by blocking ribosome binding.
Mol Microbiol: 2007, 64(6);1605-20
[PubMed:17555441]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Christine Eymann, Annette Dreisbach, Dirk Albrecht, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Sandy Gentner, Le Thi Tam, Knut Büttner, Gerrit Buurman, Christian Scharf, Simone Venz, Uwe Völker, Michael Hecker
A comprehensive proteome map of growing Bacillus subtilis cells.
Proteomics: 2004, 4(10);2849-76
[PubMed:15378759]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
D B Mirel, W F Estacio, M Mathieu, E Olmsted, J Ramirez, L M Márquez-Magaña
Environmental regulation of Bacillus subtilis sigma(D)-dependent gene expression.
J Bacteriol: 2000, 182(11);3055-62
[PubMed:10809682]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
T Caramori, A Galizzi
The UP element of the promoter for the flagellin gene, hag, stimulates transcription from both SigD- and SigA-dependent promoters in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Gen Genet: 1998, 258(4);385-8
[PubMed:9648743]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Y F Chen, J D Helmann
DNA-melting at the Bacillus subtilis flagellin promoter nucleates near -10 and expands unidirectionally.
J Mol Biol: 1997, 267(1);47-59
[PubMed:9096206]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Fredrick, T Caramori, Y F Chen, A Galizzi, J D Helmann
Promoter architecture in the flagellar regulon of Bacillus subtilis: high-level expression of flagellin by the sigma D RNA polymerase requires an upstream promoter element.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1995, 92(7);2582-6
[PubMed:7708689]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
D B Mirel, M J Chamberlin
The Bacillus subtilis flagellin gene (hag) is transcribed by the sigma 28 form of RNA polymerase.
J Bacteriol: 1989, 171(6);3095-101
[PubMed:2498284]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)