Difference between revisions of "OppD"
(→References) |
|||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
<br/><br/><br/><br/> | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
<br/><br/><br/><br/> | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
| Line 52: | Line 48: | ||
= This gene is a member of the following [[regulons]] = | = This gene is a member of the following [[regulons]] = | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[CodY regulon]]}}, | ||
{{SubtiWiki regulon|[[ScoC regulon]]}}, | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[ScoC regulon]]}}, | ||
{{SubtiWiki regulon|[[TnrA regulon]]}} | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[TnrA regulon]]}} | ||
| Line 71: | Line 68: | ||
=== Additional information=== | === Additional information=== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=The protein= | =The protein= | ||
| Line 122: | Line 116: | ||
* '''Expression browser:''' [http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/seb/viewdetail.py?id=oppD_1223455_1224531_1 oppD] {{PubMed|22383849}} | * '''Expression browser:''' [http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/seb/viewdetail.py?id=oppD_1223455_1224531_1 oppD] {{PubMed|22383849}} | ||
| − | * '''Sigma factor:''' | + | * '''[[Sigma factor]]:''' |
* '''Regulation:''' | * '''Regulation:''' | ||
| Line 131: | Line 125: | ||
** [[TnrA]]: transcription activation [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12823818 PubMed] | ** [[TnrA]]: transcription activation [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12823818 PubMed] | ||
** [[ScoC]]: transcription repression [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/10383984 PubMed] | ** [[ScoC]]: transcription repression [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/10383984 PubMed] | ||
| + | ** [[CodY]]: transcription repression, no derepression occurs, however, in a ''[[codY]]'' mutant, due to increased repression by [[ScoC]] {{PubMed|25966844}} | ||
* '''Additional information:''' | * '''Additional information:''' | ||
| Line 157: | Line 152: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed>12823818,1901616,10092453,9252573,1899858 21908671,12823818,10383984, 7997159 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>12823818,1901616,10092453,9252573,1899858 21908671,12823818,10383984, 7997159 25966844</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 13:27, 15 May 2015
- Description: oligopeptide ABC transporter (ATP-binding protein)
| Gene name | oppD |
| Synonyms | spo0KD |
| Essential | no |
| Product | oligopeptide ABC transporter (ATP-binding protein) |
| Function | initiation of sporulation, competence development |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: oppD | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: OppD | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: oppD | |
| MW, pI | 39 kDa, 6.028 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1074 bp, 358 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | oppC, oppF |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 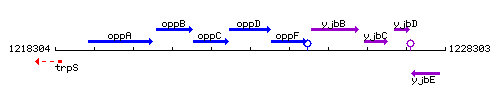
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
ABC transporters, utilization of nitrogen sources other than amino acids, genetic competence, phosphorelay, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
CodY regulon, ScoC regulon, TnrA regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU11460
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU11460
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: ABC transporter domain (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: attached to the cell membrane (via OppB-OppC) PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU11460
- Structure:
- UniProt: P24136
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 138 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 1235 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 40 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 148 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 68 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References