Difference between revisions of "MutM"
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ||
* increased susceptibility to Cr(VI) due to the accumulation of oxidative DNA damage {{PubMed|24973075}} | * increased susceptibility to Cr(VI) due to the accumulation of oxidative DNA damage {{PubMed|24973075}} | ||
| + | * absence of MutM promotes mutagenesis allowing nutritionally stressed ''B. subtilis'' cells to escape from growth limiting conditions {{PubMed|25825434}} | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| Line 137: | Line 138: | ||
<pubmed> 22933559 </pubmed> | <pubmed> 22933559 </pubmed> | ||
== Original publications == | == Original publications == | ||
| − | <pubmed> 19011023 19889642 24973075</pubmed> | + | <pubmed> 19011023 19889642 24973075 25825434</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 11:50, 1 April 2015
- Description: formamidopyrimidine-DNA glycosidase
| Gene name | mutM |
| Synonyms | ytaE |
| Essential | no |
| Product | formamidopyrimidine-DNA glycosidase |
| Function | DNA repair |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: mutM | |
| MW, pI | 31 kDa, 8.889 |
| Gene length, protein length | 834 bp, 278 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ytaF, polA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 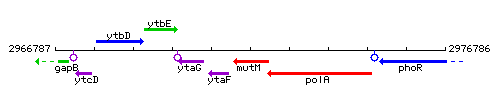
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU29080
Phenotypes of a mutant
- increased susceptibility to Cr(VI) due to the accumulation of oxidative DNA damage PubMed
- absence of MutM promotes mutagenesis allowing nutritionally stressed B. subtilis cells to escape from growth limiting conditions PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU29080
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Hydrolysis of DNA containing ring-opened 7-methylguanine residues, releasing 2,6-diamino-4-hydroxy-5-(N-methyl)formamidopyrimidine (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: FPG family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU29080
- Structure: 2F5S (complex with oxoG:C, Geobacillus stearothermophilus)
- UniProt: O34403
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number: 3.2.2.23
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Justin S Lenhart, Jeremy W Schroeder, Brian W Walsh, Lyle A Simmons
DNA repair and genome maintenance in Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2012, 76(3);530-64
[PubMed:22933559]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Original publications