Difference between revisions of "PdhC"
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
** [[PdhA]]-[[PdhB]]-[[PdhC]]-[[PdhD]] | ** [[PdhA]]-[[PdhB]]-[[PdhC]]-[[PdhD]] | ||
| − | * '''[[Localization]]:''' membrane associated [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18763711 PubMed] | + | * '''[[Localization]]:''' |
| + | ** membrane associated [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18763711 PubMed] | ||
| + | ** cytoplasm (homogeneously distributed throughout the cell) {{PubMed|24825009}} | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| Line 158: | Line 160: | ||
<pubmed> 19476487 9655937 2227213 6805383 1794583 </pubmed> | <pubmed> 19476487 9655937 2227213 6805383 1794583 </pubmed> | ||
==Original publications== | ==Original publications== | ||
| − | <pubmed>9352926,, 9352926,17726680 ,12850135 18763711 6414463 11976308 20081037 22862776 15378759</pubmed> | + | <pubmed>9352926,24825009, 9352926,17726680 ,12850135 18763711 6414463 11976308 20081037 22862776 15378759</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 17:21, 16 May 2014
- Description: pyruvate dehydrogenase (dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase E2 subunit)
| Gene name | pdhC |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | pyruvate dehydrogenase (dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase E2 subunit) |
| Function | links glycolysis and TCA cycle |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: pdhC | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: PdhC | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: pdhC | |
| MW, pI | 47 kDa, 4.855 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1326 bp, 442 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | pdhB, pdhD |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 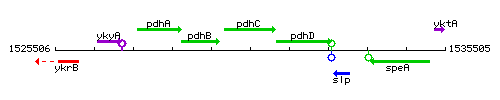
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed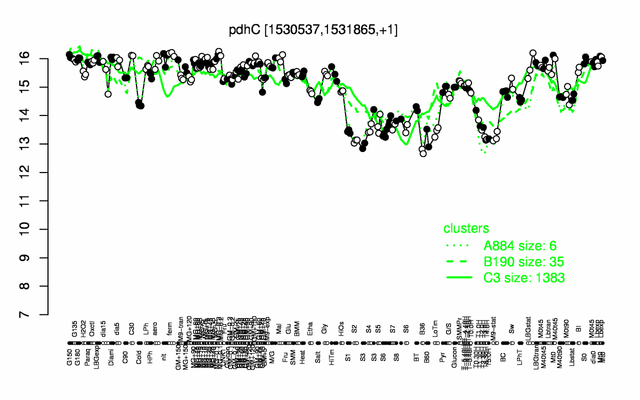
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
carbon core metabolism, membrane proteins, most abundant proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU14600
Phenotypes of a mutant
- defects in sporulation and unable to grow on glucose as single carbon source PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU14600
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Acetyl-CoA + enzyme N(6)-(dihydrolipoyl)lysine = CoA + enzyme N(6)-(S-acetyldihydrolipoyl)lysine (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: lipoyl-binding domain (according to Swiss-Prot)
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information: Michaelis-Menten PubMed
- Modification: phosphorylated (Ser/Thr/Tyr) PubMed
- Cofactors:
- lipoic acid
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Inhibited by thiamine 2-thiothiazolone diphosphate and NADH PubMed
- Low sensibility to NADPH
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU14600
- Structure: 1W88 (E1 in complex with subunit binding domain of E2, Geobacillus stearothermophilus), 2PDE (peripheral subunit binding domain, Geobacillus stearothermophilus), 1LAC (lipoyl domain, Geobacillus stearothermophilus), 1B5S (catalytic domain (residues 184-425) , Geobacillus stearothermophilus)
- UniProt: P21883
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.3.1.12 2
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- stringent response: due to presence of guanine at +1 position of the transcript PubMed
- belongs to the 100 most abundant proteins PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 11281 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 33899 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 10012 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 6860 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 6154 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Arthur Aronson, Purdue University, West Lafayette, USA homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications