Difference between revisions of "YvcI"
| Line 118: | Line 118: | ||
** A [[ncRNA]] is predicted between ''[[yvcI]]'' and ''[[trxB]]'' {{PubMed|20525796}} | ** A [[ncRNA]] is predicted between ''[[yvcI]]'' and ''[[trxB]]'' {{PubMed|20525796}} | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 67 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 67 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 601 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 472 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 816 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | |||
* '''Mutant:''' | * '''Mutant:''' | ||
Revision as of 14:22, 17 April 2014
- Description: Nudix hydrolase
| Gene name | yvcI |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | unknown |
| Function | unknown |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: yvcI | |
| MW, pI | 18 kDa, 4.993 |
| Gene length, protein length | 474 bp, 158 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yvcJ, trxB |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 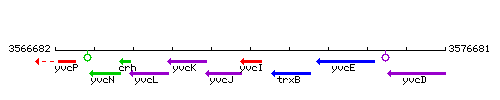
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU34780
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU34780
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: Nudix hydrolase
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU34780
- Structure:
- UniProt: O06972
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation: repressed by glucose (4.5-fold) (CcpA) PubMed, very weak stimuation of expression by citrate and succinate PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism: CcpA: transcription repression
- Additional information:
- A ncRNA is predicted between yvcI and trxB PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 67 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 601 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 472 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 816 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Irnov Irnov, Cynthia M Sharma, Jörg Vogel, Wade C Winkler
Identification of regulatory RNAs in Bacillus subtilis.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2010, 38(19);6637-51
[PubMed:20525796]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Boris Görke, Elodie Foulquier, Anne Galinier
YvcK of Bacillus subtilis is required for a normal cell shape and for growth on Krebs cycle intermediates and substrates of the pentose phosphate pathway.
Microbiology (Reading): 2005, 151(Pt 11);3777-3791
[PubMed:16272399]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hans-Matti Blencke, Georg Homuth, Holger Ludwig, Ulrike Mäder, Michael Hecker, Jörg Stülke
Transcriptional profiling of gene expression in response to glucose in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the central metabolic pathways.
Metab Eng: 2003, 5(2);133-49
[PubMed:12850135]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Galinier, J Haiech, M C Kilhoffer, M Jaquinod, J Stülke, J Deutscher, I Martin-Verstraete
The Bacillus subtilis crh gene encodes a HPr-like protein involved in carbon catabolite repression.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1997, 94(16);8439-44
[PubMed:9237995]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)