Difference between revisions of "GltA"
| Line 149: | Line 149: | ||
** [[translation]] is likely to require [[Efp]] due to the presence of several consecutive proline residues {{PubMed|23239624,23239623}} | ** [[translation]] is likely to require [[Efp]] due to the presence of several consecutive proline residues {{PubMed|23239624,23239623}} | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 2409 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 2409 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 609 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 285 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 104 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | |||
* '''Mutant:''' GP807 (del ''gltAB''::''tet''), GP222 (''gltA'' under the control of p-xyl), available in [[Stülke]] lab | * '''Mutant:''' GP807 (del ''gltAB''::''tet''), GP222 (''gltA'' under the control of p-xyl), available in [[Stülke]] lab | ||
** 1A808 ( ''gltA''::''cat''), {{PubMed|15109830}}, available at [http://pasture.asc.ohio-state.edu/BGSC/getdetail.cfm?bgscid=1A808&Search=1A808 BGSC] | ** 1A808 ( ''gltA''::''cat''), {{PubMed|15109830}}, available at [http://pasture.asc.ohio-state.edu/BGSC/getdetail.cfm?bgscid=1A808&Search=1A808 BGSC] | ||
Revision as of 14:07, 17 April 2014
- Description: large subunit of glutamate synthase
| Gene name | gltA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | glutamate synthase (large subunit) |
| Function | glutamate biosynthesis |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: gltA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: GltA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: gltA | |
| MW, pI | 168 kDa, 5.47 |
| Gene length, protein length | 4560 bp, 1520 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | gltB, gltC |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 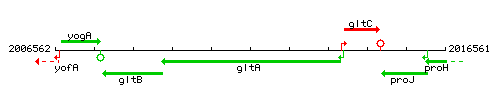
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
biosynthesis/ acquisition of amino acids, glutamate metabolism, membrane proteins, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
GltC regulon, FsrA regulon, TnrA regulon, Efp-dependent proteins
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU18450
Phenotypes of a mutant
auxotrophic for glutamate
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU18450
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: 2 L-glutamate + NADP+ = L-glutamine + 2-oxoglutarate + NADPH (according to Swiss-Prot) 2 L-glutamate + NADP(+) <=> L-glutamine + 2-oxoglutarate + NADPH
- Protein family: glutamate synthase family (according to Swiss-Prot) glutamate synthase family
- Paralogous protein(s): YerD
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Glutamine amidotransferase type-2 domain (22-415)
- Nucleotide binding domain (1060-1112)
- Modification:
- phosphorylated on Arg-904 AND/OR Arg-914 PubMed
- Cofactor(s): 3Fe-4S, FAD, FMN
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- membrane associated PubMed, cytoplasm
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU18450
- UniProt: P39812
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 1.4.1.13 3 1.4.1.13]
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
- translation is likely to require Efp due to the presence of several consecutive proline residues PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- expression activated by glucose (11 fold) (CcpA, GltC) PubMed
- repressed by arginine (GltC, RocG) PubMed
- expressed in the presence of ammonium PubMed
- repressed in the absence of good nitrogen sources (glutamine or ammonium) (TnrA) PubMed
- part of the iron sparing response, strong down-regulation in a fur mutant (Fur, FsrA) PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
- translation is likely to require Efp due to the presence of several consecutive proline residues PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 2409 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 609 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 285 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 104 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP807 (del gltAB::tet), GP222 (gltA under the control of p-xyl), available in Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Stülke lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Linc Sonenshein, Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA Homepage
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Fabian Commichau University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Katrin Gunka, Fabian M Commichau
Control of glutamate homeostasis in Bacillus subtilis: a complex interplay between ammonium assimilation, glutamate biosynthesis and degradation.
Mol Microbiol: 2012, 85(2);213-24
[PubMed:22625175]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Akira Suzuki, David B Knaff
Glutamate synthase: structural, mechanistic and regulatory properties, and role in the amino acid metabolism.
Photosynth Res: 2005, 83(2);191-217
[PubMed:16143852]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Frank M Raushel, James B Thoden, Hazel M Holden
Enzymes with molecular tunnels.
Acc Chem Res: 2003, 36(7);539-48
[PubMed:12859215]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Original publications