Difference between revisions of "Mfd"
(→Expression and regulation) |
|||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| + | * '''BsubCyc:''' [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/NEW-IMAGE?type=NIL&object=BSU00550&redirect=T BSU00550] | ||
* '''DBTBS entry:''' no entry | * '''DBTBS entry:''' no entry | ||
| Line 101: | Line 102: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| + | * '''BsubCyc:''' [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/NEW-IMAGE?type=NIL&object=BSU00550&redirect=T BSU00550] | ||
* '''Structure:''' | * '''Structure:''' | ||
Revision as of 12:46, 2 April 2014
- Description: transcription-repair coupling factor, eliminates genetic damage from transcriptionally active genes during sporulation
| Gene name | mfd |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcription-repair coupling factor |
| Function | promotes strand-specific DNA repair by displacing
RNA polymerase stalled at a nucleotide lesion and directing the (A)BC excinuclease to the RNA damage site |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: mfd | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: Mfd | |
| MW, pI | 133 kDa, 5.367 |
| Gene length, protein length | 3531 bp, 1177 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | fin, spoVT |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed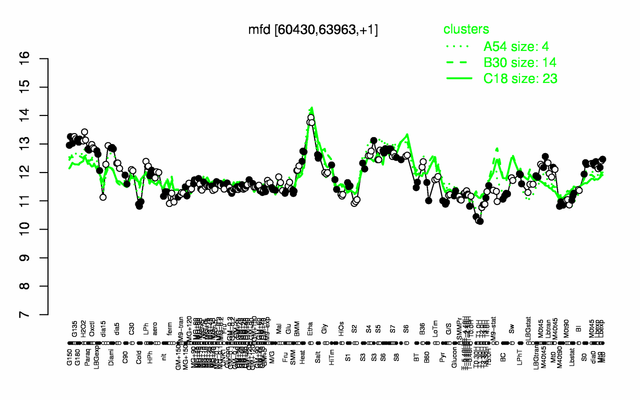
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
DNA repair/ recombination, transcription
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU00550
Phenotypes of a mutant
- in an mfd knock-out, the cell's ability to accumulate adaptive mutations in stationary phase is depressed. PubMed
- increased UV-induced mutagenesis via PolY1/ PolY2-mediated translesion synthesis PubMed
- the mutation suppresses the mucoid phenotype of motA or motB mutants PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU00550
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- promotes strand-specific DNA repair by displacing RNA polymerase stalled at a nucleotide lesion and directing the (A)BC excinuclease to the RNA damage site
- is required for roadblock transcription repression by transcription factors with binding sites downstream of the promoter (as for CcpA PubMed and CodY PubMed)
- required for the processing of genetic damage during sporulation PubMed
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s): RecG
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU00550
- Structure:
- UniProt: P37474
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulation:
- expressed throughout growth and sporulation, during sporulation both in the mother cell and the forespore PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP1167 (del ermC), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion: GP1510 (spc, based on pGP1870, pGP1389-derivative ), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- YFP fusion: GP1511 (spc, based on pGP1871, pGP1389-derivative ), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Justin S Lenhart, Jeremy W Schroeder, Brian W Walsh, Lyle A Simmons
DNA repair and genome maintenance in Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2012, 76(3);530-64
[PubMed:22933559]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ann Ganesan, Graciela Spivak, Philip C Hanawalt
Transcription-coupled DNA repair in prokaryotes.
Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci: 2012, 110;25-40
[PubMed:22749141]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Eduardo A Robleto, Holly A Martin, Mario Pedraza-Reyes
Mfd and transcriptional derepression cause genetic diversity in Bacillus subtilis.
Front Biosci (Elite Ed): 2012, 4(4);1246-54
[PubMed:22201950]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Philip C Hanawalt, Graciela Spivak
Transcription-coupled DNA repair: two decades of progress and surprises.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol: 2008, 9(12);958-70
[PubMed:19023283]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Rodrigo S Galhardo, P J Hastings, Susan M Rosenberg
Mutation as a stress response and the regulation of evolvability.
Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol: 2007, 42(5);399-435
[PubMed:17917874]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Alexandra M Deaconescu, Nigel Savery, Seth A Darst
The bacterial transcription repair coupling factor.
Curr Opin Struct Biol: 2007, 17(1);96-102
[PubMed:17239578]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
James J Truglio, Deborah L Croteau, Bennett Van Houten, Caroline Kisker
Prokaryotic nucleotide excision repair: the UvrABC system.
Chem Rev: 2006, 106(2);233-52
[PubMed:16464004]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Sergei Borukhov, Jookyung Lee, Oleg Laptenko
Bacterial transcription elongation factors: new insights into molecular mechanism of action.
Mol Microbiol: 2005, 55(5);1315-24
[PubMed:15720542]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Jeffrey Roberts, Joo-Seop Park
Mfd, the bacterial transcription repair coupling factor: translocation, repair and termination.
Curr Opin Microbiol: 2004, 7(2);120-5
[PubMed:15063847]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
E C Friedberg
Relationships between DNA repair and transcription.
Annu Rev Biochem: 1996, 65;15-42
[PubMed:8811173]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C P Selby, A Sancar
Mechanisms of transcription-repair coupling and mutation frequency decline.
Microbiol Rev: 1994, 58(3);317-29
[PubMed:7968917]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Original publications