Difference between revisions of "PpaC"
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
<br/><br/><br/><br/> | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
<br/><br/><br/><br/> | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
= [[Categories]] containing this gene/protein = | = [[Categories]] containing this gene/protein = | ||
{{SubtiWiki category|[[phosphate metabolism]]}}, | {{SubtiWiki category|[[phosphate metabolism]]}}, | ||
| − | {{SubtiWiki category|[[essential genes]]}} | + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[essential genes]]}}, |
| + | [[most abundant proteins]] | ||
= This gene is a member of the following [[regulons]] = | = This gene is a member of the following [[regulons]] = | ||
| Line 65: | Line 62: | ||
=== Additional information=== | === Additional information=== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=The protein= | =The protein= | ||
| Line 83: | Line 77: | ||
* '''Kinetic information:''' | * '''Kinetic information:''' | ||
| − | * '''Domains:''' | + | * '''[[Domains]]:''' |
* '''Modification:''' | * '''Modification:''' | ||
| Line 89: | Line 83: | ||
** Cys158 is S-bacillithiolated by NaOCl stress in B. subtilis and other Bacillus species {{PubMed|21749987}} {{PubMed|21749987}} | ** Cys158 is S-bacillithiolated by NaOCl stress in B. subtilis and other Bacillus species {{PubMed|21749987}} {{PubMed|21749987}} | ||
| − | * ''' | + | * '''[[Cofactors]]:''' |
* '''Effectors of protein activity:''' | * '''Effectors of protein activity:''' | ||
| Line 115: | Line 109: | ||
* '''Expression browser:''' [http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/seb/viewdetail.py?id=ppaC_4168204_4169133_1 ppaC] {{PubMed|22383849}} | * '''Expression browser:''' [http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/seb/viewdetail.py?id=ppaC_4168204_4169133_1 ppaC] {{PubMed|22383849}} | ||
| − | * '''Sigma factor:''' | + | * '''[[Sigma factor]]:''' |
* '''Regulation:''' | * '''Regulation:''' | ||
| Line 122: | Line 116: | ||
* '''Additional information:''' | * '''Additional information:''' | ||
| + | ** belongs to the 100 [[most abundant proteins]] {{PubMed|15378759}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| Line 143: | Line 138: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed>22938038,21749987,15533045,17611193,9845334 9782505 11342544, 9633597 21749987</pubmed> | + | <pubmed>22938038,21749987,15533045,17611193,9845334 9782505 11342544, 9633597 21749987 15378759</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 16:16, 5 March 2014
- Description: inorganic pyrophosphatase
| Gene name | ppaC |
| Synonyms | yybQ |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | inorganic pyrophosphatase |
| Function | recovery of phosphate ions from pyrophosphate |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: ppaC | |
| MW, pI | 33 kDa, 4.513 |
| Gene length, protein length | 927 bp, 309 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | hypR, yybP |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 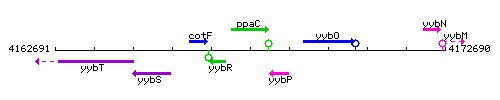
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
| Expression at a glance PubMed 500px | |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
phosphate metabolism, essential genes, most abundant proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU40550
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Diphosphate + H2O = 2 phosphate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: PPase class C family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- UniProt: P37487
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 3.6.1.1
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: ppaC (according to DBTBS)
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- belongs to the 100 most abundant proteins PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References