Difference between revisions of "SpoIIID"
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[mbl]]'', ''[[usd]]'' | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[mbl]]'', ''[[usd]]'' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''Sequences'''||[http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence-aa?type=GENE&object=BSU36420 Protein] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence?type=GENE&object=BSU36420 DNA] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/seq-selector?chromosome=CHROM-1&object=BSU36420 | + | |style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''Sequences'''||[http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence-aa?type=GENE&object=BSU36420 Protein] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence?type=GENE&object=BSU36420 DNA] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/seq-selector?chromosome=CHROM-1&object=BSU36420 DNA_with_flanks] |
|- | |- | ||
|colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:spoIIID_context.gif]] | |colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:spoIIID_context.gif]] | ||
Revision as of 11:28, 14 May 2013
- Description: transcriptional regulator (repressor or activator) of a subset of sigma-E-dependent genes
| Gene name | spoIIID |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional regulator |
| Function | regulation of mother cell gene expression |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: spoIIID | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Asp, Asn, Cell wall | |
| MW, pI | 10 kDa, 9.496 |
| Gene length, protein length | 279 bp, 93 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | mbl, usd |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 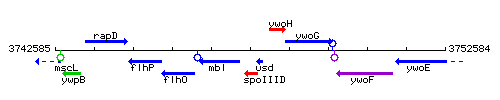
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed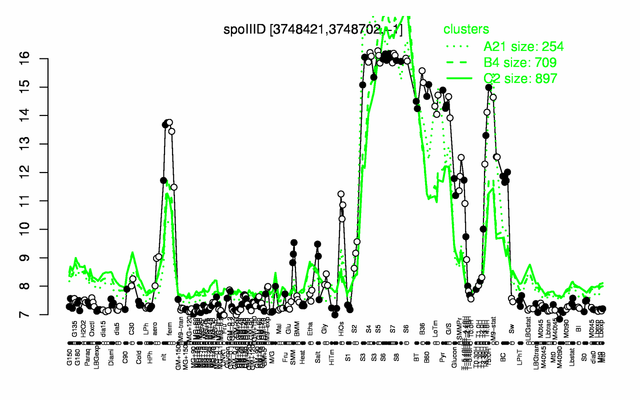
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transcription factors and their control, sporulation proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The SpoIIID regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU36420
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: binds its DNA targets as a monomeric protein (possible due to the two DNA-binding motifs) PubMed
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains: two DNA-binding regions: HTH at the N-terminus and a basic region near the C-terminus PubMed
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure: 2L0K (complex with DNA)
- UniProt: P15281
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Additional publications: PubMed
Paul Himes, Steven J McBryant, Lee Kroos
Two regions of Bacillus subtilis transcription factor SpoIIID allow a monomer to bind DNA.
J Bacteriol: 2010, 192(6);1596-606
[PubMed:20061473]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Lijuan Wang, John Perpich, Adam Driks, Lee Kroos
One perturbation of the mother cell gene regulatory network suppresses the effects of another during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2007, 189(23);8467-73
[PubMed:17890309]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Chris Guillot, Charles P Moran
Essential internal promoter in the spoIIIA locus of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2007, 189(20);7181-9
[PubMed:17693505]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Lijuan Wang, John Perpich, Adam Driks, Lee Kroos
Maintaining the transcription factor SpoIIID level late during sporulation causes spore defects in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2007, 189(20);7302-9
[PubMed:17693499]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Patrick Eichenberger, Masaya Fujita, Shane T Jensen, Erin M Conlon, David Z Rudner, Stephanie T Wang, Caitlin Ferguson, Koki Haga, Tsutomu Sato, Jun S Liu, Richard Losick
The program of gene transcription for a single differentiating cell type during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
PLoS Biol: 2004, 2(10);e328
[PubMed:15383836]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
H Ichikawa, L Kroos
Combined action of two transcription factors regulates genes encoding spore coat proteins of Bacillus subtilis.
J Biol Chem: 2000, 275(18);13849-55
[PubMed:10788508]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Decatur, M T McMurry, B N Kunkel, R Losick
Translation of the mRNA for the sporulation gene spoIIID of Bacillus subtilis is dependent upon translation of a small upstream open reading frame.
J Bacteriol: 1997, 179(4);1324-8
[PubMed:9023218]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
B Zhang, R A Daniel, J Errington, L Kroos
Bacillus subtilis SpoIIID protein binds to two sites in the spoVD promoter and represses transcription by sigmaE RNA polymerase.
J Bacteriol: 1997, 179(3);972-5
[PubMed:9006059]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
R Halberg, V Oke, L Kroos
Effects of Bacillus subtilis sporulation regulatory protein SpoIIID on transcription by sigma K RNA polymerase in vivo and in vitro.
J Bacteriol: 1995, 177(7);1888-91
[PubMed:7896717]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Y Abhayawardhane, G C Stewart
Bacillus subtilis possesses a second determinant with extensive sequence similarity to the Escherichia coli mreB morphogene.
J Bacteriol: 1995, 177(3);765-73
[PubMed:7836311]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
R Halberg, L Kroos
Sporulation regulatory protein SpoIIID from Bacillus subtilis activates and represses transcription by both mother-cell-specific forms of RNA polymerase.
J Mol Biol: 1994, 243(3);425-36
[PubMed:7966271]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
P A Levin, N Fan, E Ricca, A Driks, R Losick, S Cutting
An unusually small gene required for sporulation by Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 1993, 9(4);761-71
[PubMed:8231808]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
R Halberg, L Kroos
Fate of the SpoIIID switch protein during Bacillus subtilis sporulation depends on the mother-cell sigma factor, sigma K.
J Mol Biol: 1992, 228(3);840-9
[PubMed:1469717]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L Zheng, R Halberg, S Roels, H Ichikawa, L Kroos, R Losick
Sporulation regulatory protein GerE from Bacillus subtilis binds to and can activate or repress transcription from promoters for mother-cell-specific genes.
J Mol Biol: 1992, 226(4);1037-50
[PubMed:1518043]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K M Tatti, C H Jones, C P Moran
Genetic evidence for interaction of sigma E with the spoIIID promoter in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1991, 173(24);7828-33
[PubMed:1744038]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Cutting, A Driks, R Schmidt, B Kunkel, R Losick
Forespore-specific transcription of a gene in the signal transduction pathway that governs Pro-sigma K processing in Bacillus subtilis.
Genes Dev: 1991, 5(3);456-66
[PubMed:1900494]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L B Zheng, R Losick
Cascade regulation of spore coat gene expression in Bacillus subtilis.
J Mol Biol: 1990, 212(4);645-60
[PubMed:1691789]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C M Stevens, J Errington
Differential gene expression during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis: structure and regulation of the spoIIID gene.
Mol Microbiol: 1990, 4(4);543-51
[PubMed:2112673]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
B Kunkel, L Kroos, H Poth, P Youngman, R Losick
Temporal and spatial control of the mother-cell regulatory gene spoIIID of Bacillus subtilis.
Genes Dev: 1989, 3(11);1735-44
[PubMed:2514119]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)