Difference between revisions of "Mbl"
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[flhO]]'', ''[[spoIIID]]'' | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[flhO]]'', ''[[spoIIID]]'' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''Sequences'''||[http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence-aa?type=GENE&object=BSU36410 Protein] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence?type=GENE&object=BSU36410 DNA] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/seq-selector?chromosome=CHROM-1&object=BSU36410 | + | |style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''Sequences'''||[http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence-aa?type=GENE&object=BSU36410 Protein] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence?type=GENE&object=BSU36410 DNA] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/seq-selector?chromosome=CHROM-1&object=BSU36410 DNA_with_flanks] |
|- | |- | ||
|colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:mbl_context.gif]] | |colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:mbl_context.gif]] | ||
Revision as of 11:28, 14 May 2013
- Description: cell shape-determining protein, forms filaments, the polymers control/restrict the mobility of the cell wall elongation enzyme complex
| Gene name | mbl |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | MreB-like protein |
| Function | cell shape determination |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: mbl | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: Mbl | |
| MW, pI | 35 kDa, 5.669 |
| Gene length, protein length | 999 bp, 333 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | flhO, spoIIID |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 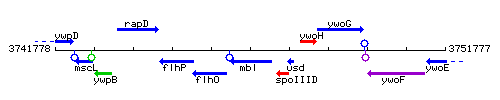
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell shape, sporulation proteins, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
SigE regulon, stringent response
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU36410
Phenotypes of a mutant
non-viable in the presence of low Mg(2+), readily accumulate rsgI suppressor mutants PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- forms helical filaments in a heterologous system PubMed
- Protein family: ftsA/mreB family (according to Swiss-Prot)
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- during logarithmic growth, Mbl forms discrete patches that move processively along peripheral tracks perpendicular to the cell axis PubMed
- forms transverse bands as cells enter the stationary phase PubMed
- close to the inner surface of the cytoplasmic membrane PubMed
- reports on helical structures formed by Mbl PubMed seem to be misinterpretation of data PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P39751
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- An antisense RNA is predicted for mbl PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Görke lab
- Antibody: available in the Jeff Errington and Peter Graumann labs
Labs working on this gene/protein
Peter Graumann, Freiburg University, Germany homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Localization
Other original publications
Siyuan Wang, Leon Furchtgott, Kerwyn Casey Huang, Joshua W Shaevitz
Helical insertion of peptidoglycan produces chiral ordering of the bacterial cell wall.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2012, 109(10);E595-604
[PubMed:22343529]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Erin Treece, Andrew Pinkham, Thomas Kim
Aminoguanidine down-regulates the expression of mreB-like protein in Bacillus subtilis.
Curr Microbiol: 2012, 64(2);112-7
[PubMed:22048160]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hervé Joël Defeu Soufo, Peter L Graumann
Bacillus subtilis MreB paralogues have different filament architectures and lead to shape remodelling of a heterologous cell system.
Mol Microbiol: 2010, 78(5);1145-58
[PubMed:21091501]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Irnov Irnov, Cynthia M Sharma, Jörg Vogel, Wade C Winkler
Identification of regulatory RNAs in Bacillus subtilis.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2010, 38(19);6637-51
[PubMed:20525796]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yoshikazu Kawai, Kei Asai, Jeffery Errington
Partial functional redundancy of MreB isoforms, MreB, Mbl and MreBH, in cell morphogenesis of Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2009, 73(4);719-31
[PubMed:19659933]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kathrin Schirner, Jeff Errington
Influence of heterologous MreB proteins on cell morphology of Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 2009, 155(Pt 11);3611-3621
[PubMed:19643765]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kathrin Schirner, Jeff Errington
The cell wall regulator {sigma}I specifically suppresses the lethal phenotype of mbl mutants in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2009, 191(5);1404-13
[PubMed:19114499]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Rut Carballido-López, Alex Formstone, Ying Li, S Dusko Ehrlich, Philippe Noirot, Jeff Errington
Actin homolog MreBH governs cell morphogenesis by localization of the cell wall hydrolase LytE.
Dev Cell: 2006, 11(3);399-409
[PubMed:16950129]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Kittichoat Tiyanont, Thierry Doan, Michael B Lazarus, Xiao Fang, David Z Rudner, Suzanne Walker
Imaging peptidoglycan biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis with fluorescent antibiotics.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2006, 103(29);11033-8
[PubMed:16832063]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Mark Leaver, Jeff Errington
Roles for MreC and MreD proteins in helical growth of the cylindrical cell wall in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2005, 57(5);1196-209
[PubMed:16101995]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Richard A Daniel, Jeff Errington
Control of cell morphogenesis in bacteria: two distinct ways to make a rod-shaped cell.
Cell: 2003, 113(6);767-76
[PubMed:12809607]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Rut Carballido-López, Jeff Errington
The bacterial cytoskeleton: in vivo dynamics of the actin-like protein Mbl of Bacillus subtilis.
Dev Cell: 2003, 4(1);19-28
[PubMed:12530960]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L J Jones, R Carballido-López, J Errington
Control of cell shape in bacteria: helical, actin-like filaments in Bacillus subtilis.
Cell: 2001, 104(6);913-22
[PubMed:11290328]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Decatur, M T McMurry, B N Kunkel, R Losick
Translation of the mRNA for the sporulation gene spoIIID of Bacillus subtilis is dependent upon translation of a small upstream open reading frame.
J Bacteriol: 1997, 179(4);1324-8
[PubMed:9023218]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Y Abhayawardhane, G C Stewart
Bacillus subtilis possesses a second determinant with extensive sequence similarity to the Escherichia coli mreB morphogene.
J Bacteriol: 1995, 177(3);765-73
[PubMed:7836311]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)