Difference between revisions of "MinD"
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || septum placement | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || septum placement | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Gene expression levels in [http:// | + | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Gene expression levels in [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/apps/expression/ ''Subti''Express]''': [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/apps/expression/expression.php?search=BSU27990 minD] |
|- | |- | ||
|colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Interactions involving this protein in [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtinteract/startpage/start/ ''Subt''Interact]''': [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtinteract/interactionList/2/MinD MinD] | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Interactions involving this protein in [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtinteract/startpage/start/ ''Subt''Interact]''': [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtinteract/interactionList/2/MinD MinD] | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[spoIVFA]]'', ''[[minC]]'' | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[spoIVFA]]'', ''[[minC]]'' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''Sequences'''||[http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence-aa?type=GENE&object=BSU27990 Protein] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence?type=GENE&object=BSU27990 DNA] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/seq-selector?chromosome=CHROM-1&object=BSU27990 Advanced_DNA] |
|- | |- | ||
|colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:minD_context.gif]] | |colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:minD_context.gif]] | ||
Revision as of 13:28, 13 May 2013
- Description: cell-division inhibitor (septum placement), part of the Min system (with DivIVA, MinC, MinJ), Noc and the Min system ensure the efficient utilization of the division site at midcell in by ensuring Z ring placement
| Gene name | minD |
| Synonyms | divIVB1 |
| Essential | no |
| Product | cell-division inhibitor |
| Function | septum placement |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: minD | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: MinD | |
| MW, pI | 29 kDa, 4.984 |
| Gene length, protein length | 804 bp, 268 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | spoIVFA, minC |
| Sequences | Protein DNA Advanced_DNA |
Genetic context 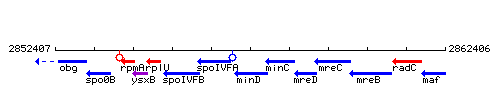
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell division, cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, V, W, X, Y), membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU27990
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
- A mutation was found in this gene after evolution under relaxed selection for sporulation PubMed
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: The Min system prevents minicell formation adjacent to recently completed division sites by promoting the disassembly of the cytokinetic ring, thereby ensuring that cell division occurs only once per cell cycle PubMed
- Protein family: MinD subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: Q01464
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original Publications
Additional publications: PubMed