Difference between revisions of "YhdY"
Raphael2215 (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
<br/><br/><br/><br/> | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
<br/><br/><br/><br/> | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/> | <br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
| Line 144: | Line 140: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
==Reviews== | ==Reviews== | ||
| − | <pubmed>12626684 ,, </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>12626684 , 22685280, </pubmed> |
==Original Publications== | ==Original Publications== | ||
<big>''Lehnik-Habrink M, Schaffer M, Mäder U, Diethmaier C, Herzberg C, Stülke J'' </big> | <big>''Lehnik-Habrink M, Schaffer M, Mäder U, Diethmaier C, Herzberg C, Stülke J'' </big> | ||
Revision as of 08:00, 29 August 2012
- Description: mechanosensitive channel, similar to MscS
| Gene name | yhdY |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | mechanosensitive channel, similar to MscS |
| Function | resistance to osmotic downshock |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: yhdY | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Stress | |
| MW, pI | 42 kDa, 5.758 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1113 bp, 371 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yhdX, srtN |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 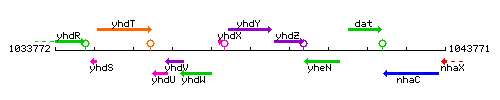
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed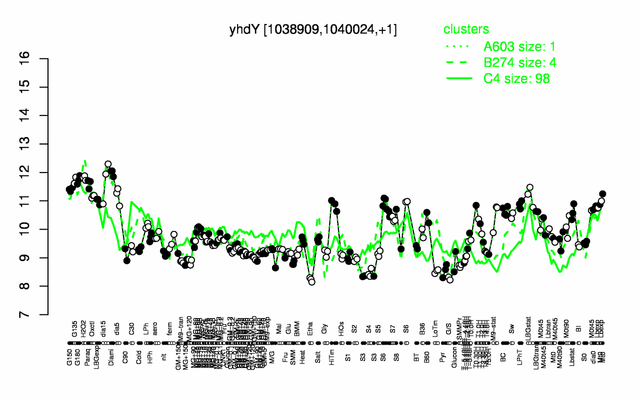
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
coping with hypo-osmotic stress, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU09640
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: O07594
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Erhard Bremer, University of Marburg, Germany homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original Publications
Lehnik-Habrink M, Schaffer M, Mäder U, Diethmaier C, Herzberg C, Stülke J RNA processing in Bacillus subtilis: identification of targets of the essential RNase Y. Mol Microbiol. 2011 81(6): 1459-1473. PubMed:21815947