Difference between revisions of "SpoIVA"
(→This gene is a member of the following regulons) |
|||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
= This gene is a member of the following [[regulons]] = | = This gene is a member of the following [[regulons]] = | ||
| − | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[SigE regulon]]}} | + | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[SigE regulon]]}}, |
| + | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[SpoIIID regulon]]}} | ||
=The gene= | =The gene= | ||
Revision as of 15:56, 29 July 2012
- Description: spore coat morphogenetic protein, anchors the spore coat to the spore surface via SpoVM
| Gene name | spoIVA |
| Synonyms | spoVP |
| Essential | no |
| Product | basement layer protein for spore coat assembly |
| Function | spore cortex formation and coat assembly |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: SpoIVA | |
| MW, pI | 55 kDa, 4.546 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1476 bp, 492 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | hbs, yphF |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 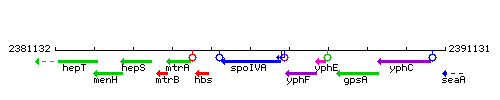
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed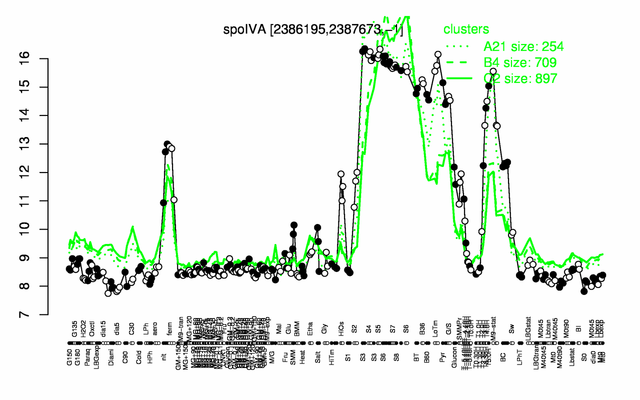
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU22800
Phenotypes of a mutant
- the spore coat does not localize to the spore surface but self-assembles into aggregates in the mother cell cytoplasm PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- spore coat PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P35149
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: spoIVA PubMed
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Additional publications: PubMed
Peter T McKenney, Patrick Eichenberger
Dynamics of spore coat morphogenesis in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2012, 83(2);245-60
[PubMed:22171814]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Katherine H Wang, Anabela L Isidro, Lia Domingues, Haig A Eskandarian, Peter T McKenney, Kevin Drew, Paul Grabowski, Ming-Hsiu Chua, Samantha N Barry, Michelle Guan, Richard Bonneau, Adriano O Henriques, Patrick Eichenberger
The coat morphogenetic protein SpoVID is necessary for spore encasement in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2009, 74(3);634-49
[PubMed:19775244]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kumaran S Ramamurthi, Richard Losick
ATP-driven self-assembly of a morphogenetic protein in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Cell: 2008, 31(3);406-14
[PubMed:18691972]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kumaran S Ramamurthi, Katie Rose Clapham, Richard Losick
Peptide anchoring spore coat assembly to the outer forespore membrane in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2006, 62(6);1547-57
[PubMed:17427285]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Leif Steil, Mónica Serrano, Adriano O Henriques, Uwe Völker
Genome-wide analysis of temporally regulated and compartment-specific gene expression in sporulating cells of Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 2005, 151(Pt 2);399-420
[PubMed:15699190]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Katerina Ragkousi, Patrick Eichenberger, Christiaan van Ooij, Peter Setlow
Identification of a new gene essential for germination of Bacillus subtilis spores with Ca2+-dipicolinate.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(7);2315-29
[PubMed:12644503]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K D Price, R Losick
A four-dimensional view of assembly of a morphogenetic protein during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(3);781-90
[PubMed:9922240]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Peter J Lewis, Jeffery Errington
Use of green fluorescent protein for detection of cell-specific gene expression and subcellular protein localization during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 1996, 142 ( Pt 4);733-740
[PubMed:8936302]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
K Pogliano, E Harry, R Losick
Visualization of the subcellular location of sporulation proteins in Bacillus subtilis using immunofluorescence microscopy.
Mol Microbiol: 1995, 18(3);459-70
[PubMed:8748030]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C D Webb, A Decatur, A Teleman, R Losick
Use of green fluorescent protein for visualization of cell-specific gene expression and subcellular protein localization during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1995, 177(20);5906-11
[PubMed:7592342]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Driks, S Roels, B Beall, C P Moran, R Losick
Subcellular localization of proteins involved in the assembly of the spore coat of Bacillus subtilis.
Genes Dev: 1994, 8(2);234-44
[PubMed:8299942]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C M Stevens, R Daniel, N Illing, J Errington
Characterization of a sporulation gene, spoIVA, involved in spore coat morphogenesis in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1992, 174(2);586-94
[PubMed:1729247]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Roels, A Driks, R Losick
Characterization of spoIVA, a sporulation gene involved in coat morphogenesis in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1992, 174(2);575-85
[PubMed:1729246]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L B Zheng, R Losick
Cascade regulation of spore coat gene expression in Bacillus subtilis.
J Mol Biol: 1990, 212(4);645-60
[PubMed:1691789]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)