Difference between revisions of "GltA"
(→Extended information on the protein) |
(→References) |
||
| Line 156: | Line 156: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | + | ==Reviews== | |
| + | <pubmed>16143852 12859215</pubmed> | ||
| + | ==Original publications== | ||
<pubmed>12823818,18199747 ,11029411,12850135 7559360 15150225 2548995 17183217, 17608797,17134717,14523131,12823818, 18326565,17981983,18763711 20933603 17012385 </pubmed> | <pubmed>12823818,18199747 ,11029411,12850135 7559360 15150225 2548995 17183217, 17608797,17134717,14523131,12823818, 18326565,17981983,18763711 20933603 17012385 </pubmed> | ||
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 10:23, 26 December 2011
- Description: large subunit of glutamate synthase
| Gene name | gltA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | glutamate synthase (large subunit) |
| Function | glutamate biosynthesis |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: GltA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Ammonium/ glutamate | |
| MW, pI | 168 kDa, 5.47 |
| Gene length, protein length | 4560 bp, 1520 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | gltB, gltC |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 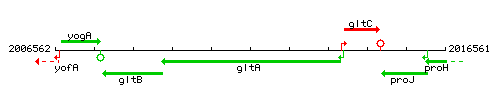
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
biosynthesis/ acquisition of amino acids, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU18450
Phenotypes of a mutant
auxotrophic for glutamate
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: 2 L-glutamate + NADP+ = L-glutamine + 2-oxoglutarate + NADPH (according to Swiss-Prot) 2 L-glutamate + NADP(+) <=> L-glutamine + 2-oxoglutarate + NADPH
- Protein family: glutamate synthase family (according to Swiss-Prot) glutamate synthase family
- Paralogous protein(s): YerD
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Glutamine amidotransferase type-2 domain (22-415)
- Nucleotide binding domain (1060-1112)
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s): 3Fe-4S, FAD, FMN
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: membrane associated PubMed, cytoplasm
Database entries
- UniProt: P39812
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 1.4.1.13 3 1.4.1.13]
Additional information
subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information: subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP807 (del gltAB::tet), GP222 (gltA under the control of p-xyl), available in Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Stülke lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Linc Sonenshein, Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA Homepage
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
Frederik M Meyer, Jan Gerwig, Elke Hammer, Christina Herzberg, Fabian M Commichau, Uwe Völker, Jörg Stülke
Physical interactions between tricarboxylic acid cycle enzymes in Bacillus subtilis: evidence for a metabolon.
Metab Eng: 2011, 13(1);18-27
[PubMed:20933603]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hannes Hahne, Susanne Wolff, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
From complementarity to comprehensiveness--targeting the membrane proteome of growing Bacillus subtilis by divergent approaches.
Proteomics: 2008, 8(19);4123-36
[PubMed:18763711]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Fabian M Commichau, Katrin Gunka, Jens J Landmann, Jörg Stülke
Glutamate metabolism in Bacillus subtilis: gene expression and enzyme activities evolved to avoid futile cycles and to allow rapid responses to perturbations of the system.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(10);3557-64
[PubMed:18326565]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Magali Cottevieille, Eric Larquet, Slavica Jonic, Maxim V Petoukhov, Gianluca Caprini, Stefano Paravisi, Dmitri I Svergun, Maria A Vanoni, Nicolas Boisset
The subnanometer resolution structure of the glutamate synthase 1.2-MDa hexamer by cryoelectron microscopy and its oligomerization behavior in solution: functional implications.
J Biol Chem: 2008, 283(13);8237-49
[PubMed:18199747]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ulf Gerth, Holger Kock, Ilja Kusters, Stephan Michalik, Robert L Switzer, Michael Hecker
Clp-dependent proteolysis down-regulates central metabolic pathways in glucose-starved Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(1);321-31
[PubMed:17981983]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Fabian M Commichau, Christina Herzberg, Philipp Tripal, Oliver Valerius, Jörg Stülke
A regulatory protein-protein interaction governs glutamate biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis: the glutamate dehydrogenase RocG moonlights in controlling the transcription factor GltC.
Mol Microbiol: 2007, 65(3);642-54
[PubMed:17608797]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Fabian M Commichau, Ingrid Wacker, Jan Schleider, Hans-Matti Blencke, Irene Reif, Philipp Tripal, Jörg Stülke
Characterization of Bacillus subtilis mutants with carbon source-independent glutamate biosynthesis.
J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol: 2007, 12(1-2);106-13
[PubMed:17183217]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Silvia Picossi, Boris R Belitsky, Abraham L Sonenshein
Molecular mechanism of the regulation of Bacillus subtilis gltAB expression by GltC.
J Mol Biol: 2007, 365(5);1298-313
[PubMed:17134717]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Marcus Miethke, Helga Westers, Evert-Jan Blom, Oscar P Kuipers, Mohamed A Marahiel
Iron starvation triggers the stringent response and induces amino acid biosynthesis for bacillibactin production in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2006, 188(24);8655-7
[PubMed:17012385]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Boris R Belitsky, Abraham L Sonenshein
Modulation of activity of Bacillus subtilis regulatory proteins GltC and TnrA by glutamate dehydrogenase.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(11);3399-407
[PubMed:15150225]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ingrid Wacker, Holger Ludwig, Irene Reif, Hans-Matti Blencke, Christian Detsch, Jörg Stülke
The regulatory link between carbon and nitrogen metabolism in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the gltAB operon by the catabolite control protein CcpA.
Microbiology (Reading): 2003, 149(Pt 10);3001-3009
[PubMed:14523131]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hans-Matti Blencke, Georg Homuth, Holger Ludwig, Ulrike Mäder, Michael Hecker, Jörg Stülke
Transcriptional profiling of gene expression in response to glucose in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the central metabolic pathways.
Metab Eng: 2003, 5(2);133-49
[PubMed:12850135]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ken-ichi Yoshida, Hirotake Yamaguchi, Masaki Kinehara, Yo-hei Ohki, Yoshiko Nakaura, Yasutaro Fujita
Identification of additional TnrA-regulated genes of Bacillus subtilis associated with a TnrA box.
Mol Microbiol: 2003, 49(1);157-65
[PubMed:12823818]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
B R Belitsky, L V Wray, S H Fisher, D E Bohannon, A L Sonenshein
Role of TnrA in nitrogen source-dependent repression of Bacillus subtilis glutamate synthase gene expression.
J Bacteriol: 2000, 182(21);5939-47
[PubMed:11029411]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
B R Belitsky, A L Sonenshein
Mutations in GltC that increase Bacillus subtilis gltA expression.
J Bacteriol: 1995, 177(19);5696-700
[PubMed:7559360]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
D E Bohannon, A L Sonenshein
Positive regulation of glutamate biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1989, 171(9);4718-27
[PubMed:2548995]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)