Difference between revisions of "OppC"
(→Extended information on the protein) |
|||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
* '''Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:''' | * '''Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:''' | ||
| + | ** required for the uptake of quorum sensing peptides such as [[PhrH]] {{PubMed|21908671}} | ||
* '''Protein family:''' ABC transmembrane type-1 domain (according to Swiss-Prot) | * '''Protein family:''' ABC transmembrane type-1 domain (according to Swiss-Prot) | ||
| Line 139: | Line 140: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | + | '''Additional publications:''' {{PubMed|21908671}} | |
<pubmed>12823818,1901616,10092453,9252573,,12823818,10383984, 7997159 </pubmed> | <pubmed>12823818,1901616,10092453,9252573,,12823818,10383984, 7997159 </pubmed> | ||
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 18:28, 16 September 2011
- Description: oligopeptide ABC transporter (permease)
| Gene name | oppC |
| Synonyms | spo0KC |
| Essential | no |
| Product | oligopeptide ABC transporter (permease) |
| Function | initiation of sporulation, competence development |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: OppC | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Alternative nitrogen sources | |
| MW, pI | 33 kDa, 10.107 |
| Gene length, protein length | 915 bp, 305 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | oppB, oppD |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 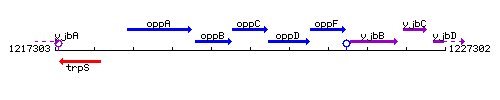
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
ABC transporters, utilization of nitrogen sources other than amino acids, genetic competence, phosphorelay, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU11450
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: ABC transmembrane type-1 domain (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cell membrane PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P24139
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Additional publications: PubMed
Ken-ichi Yoshida, Hirotake Yamaguchi, Masaki Kinehara, Yo-hei Ohki, Yoshiko Nakaura, Yasutaro Fujita
Identification of additional TnrA-regulated genes of Bacillus subtilis associated with a TnrA box.
Mol Microbiol: 2003, 49(1);157-65
[PubMed:12823818]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Koide, M Perego, J A Hoch
ScoC regulates peptide transport and sporulation initiation in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(13);4114-7
[PubMed:10383984]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Y Quentin, G Fichant, F Denizot
Inventory, assembly and analysis of Bacillus subtilis ABC transport systems.
J Mol Biol: 1999, 287(3);467-84
[PubMed:10092453]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J R LeDeaux, J M Solomon, A D Grossman
Analysis of non-polar deletion mutations in the genes of the spo0K (opp) operon of Bacillus subtilis.
FEMS Microbiol Lett: 1997, 153(1);63-9
[PubMed:9252573]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Koide, J A Hoch
Identification of a second oligopeptide transport system in Bacillus subtilis and determination of its role in sporulation.
Mol Microbiol: 1994, 13(3);417-26
[PubMed:7997159]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Perego, C F Higgins, S R Pearce, M P Gallagher, J A Hoch
The oligopeptide transport system of Bacillus subtilis plays a role in the initiation of sporulation.
Mol Microbiol: 1991, 5(1);173-85
[PubMed:1901616]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)