Difference between revisions of "SufS"
(→Extended information on the protein) |
(→Basic information/ Evolution) |
||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
* '''Protein family:''' Csd subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot) | * '''Protein family:''' Csd subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot) | ||
| − | * '''Paralogous protein(s):''' [[NifS]], [[YrvO]], [[NifZ]] | + | * '''Paralogous protein(s):''' [[NifS]], [[YrvO]], [[NifZ]], [[YcbU]] |
=== Extended information on the protein === | === Extended information on the protein === | ||
Revision as of 09:09, 2 July 2011
- Description: cysteine desulfurase
| Gene name | sufS |
| Synonyms | yurW, csd |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | cysteine desulfurase |
| Function | formation of iron-sulfur clusters in proteins |
| MW, pI | 44 kDa, 5.199 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1218 bp, 406 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | sufU, sufD |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 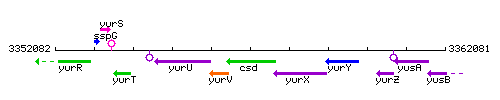
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
iron metabolism, essential genes
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU32690
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Protein family: Csd subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot)
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: O32164
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number: 2.8.1.7
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Bruna Selbach, Emily Earles, Patricia C Dos Santos
Kinetic analysis of the bisubstrate cysteine desulfurase SufS from Bacillus subtilis.
Biochemistry: 2010, 49(40);8794-802
[PubMed:20822158]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Alexander G Albrecht, Daili J A Netz, Marcus Miethke, Antonio J Pierik, Olaf Burghaus, Florian Peuckert, Roland Lill, Mohamed A Marahiel
SufU is an essential iron-sulfur cluster scaffold protein in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2010, 192(6);1643-51
[PubMed:20097860]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Additional publications: PubMed