Difference between revisions of "LexA"
(→This gene is a member of the following regulons) |
(→Expression and regulation) |
||
| Line 100: | Line 100: | ||
* '''Operon:''' ''[[lexA]]'' {{PubMed|1657879}} | * '''Operon:''' ''[[lexA]]'' {{PubMed|1657879}} | ||
| − | * '''[[Sigma factor]]:''' | + | * '''[[Sigma factor]]:''' |
* '''Regulation:''' | * '''Regulation:''' | ||
Revision as of 18:58, 20 May 2011
- Description: transcriptional repressor of the SOS regulon
| Gene name | lexA |
| Synonyms | dinR |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional repressor of the SOS regulon |
| Function | regulation of DNA damage repair |
| Function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Phosphorelay, Protein secretion | |
| MW, pI | 22 kDa, 5.155 |
| Gene length, protein length | 615 bp, 205 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | fosB, yneA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 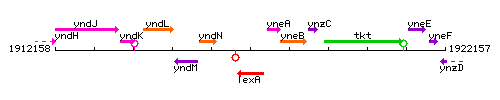
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
DNA repair/ recombination, transcription factors and their control, general stress proteins (controlled by SigB)
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The LexA regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU17850
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Represses uvrB, dinB, dinC, recA genes and itself by binding to the 14 bp palindromic sequence 5'-CGAACNNNNGTTCG-3'. In the presence of single-stranded DNA, RecA interacts with LexA causing an autocatalytic cleavage which disrupts the DNA-binding part of LexA, leading to derepression of the SOS regulon and eventually DNA repair. (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: peptidase S24 family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- UniProt: P31080
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References