Difference between revisions of "PtsI"
Czschiedrich (talk | contribs) (→Biological materials) |
Czschiedrich (talk | contribs) (→Biological materials) |
||
| Line 117: | Line 117: | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | * '''Mutant:''' GP864 (ermC) | + | * '''Mutant:''' available in [[Stülke]] lab |
| + | ** GP864 (ermC) | ||
| + | ** GP778 (replacement of ''glcT'' and the ''ptsGHI'' operon by a spc cassette) | ||
* '''Expression vector:''' | * '''Expression vector:''' | ||
Revision as of 13:15, 13 September 2010
- Description: Enzyme I, general (non sugar-specific) component of the PTS. Enzyme I transfers the phosphoryl group from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to the phosphoryl carrier protein (HPr)
| Gene name | ptsI |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | phosphotransferase system (PTS) enzyme I |
| Function | PTS-dependent sugar transport |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Central C-metabolism | |
| MW, pI | 62,9 kDa, 4.59 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1710 bp, 570 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | ptsH, splA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 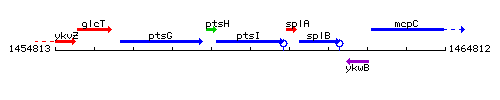
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU13910
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Phosphoenolpyruvate + protein L-histidine = pyruvate + protein N(pi)-phospho-L-histidine (according to Swiss-Prot) PEP-dependent autophosphorylation on His-189, transfer of the phosphoryl group to HPr (His-15)
- Protein family: PEP-utilizing enzyme family (according to Swiss-Prot) PEP-utilizing enzyme family
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- HPr binding site (N-Terminal Domain)
- pyruvate binding site (C-Terminal Domain)
- pyrophosphate/phosphate carrier histidine (central Domain)
- Modification:
- transient autophosphorylation on His-189
- in vivo also phosphorylated on Ser-34 or Ser-36 PubMed
- Cofactor(s): Magnesium
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- UniProt: P08838
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.7.3.9 2.7.3.9]
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- ptsG: transcriptional antitermination via the GlcT-dependent RNA switch PubMed
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: available in Stülke lab
- GP864 (ermC)
- GP778 (replacement of glcT and the ptsGHI operon by a spc cassette)
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Josef Deutscher, Paris-Grignon, France
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References