Difference between revisions of "MetE"
(→Database entries) |
(→References) |
||
| Line 123: | Line 123: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed>19258532,16194229,10094622,17611193,,17726680 12107147, </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>19258532,16194229,10094622,17611193,18039762 ,17726680 12107147, </pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 06:45, 24 February 2010
- Description: methionine synthase
| Gene name | metE |
| Synonyms | metC |
| Essential | no |
| Product | methionine synthase |
| Function | biosynthesis of methionine |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Cys, Met & Sulfate assimilation | |
| MW, pI | 86 kDa, 4.839 |
| Gene length, protein length | 2286 bp, 762 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | guaD, ispA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 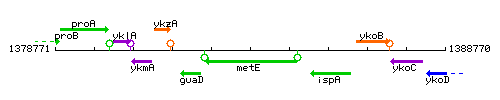
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU13180
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: 5-methyltetrahydropteroyltri-L-glutamate + L-homocysteine = tetrahydropteroyltri-L-glutamate + L-methionine (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: vitamin-B12 independent methionine synthase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification: phosphorylated on ser/ thr/ tyr PubMed, S-cysteinylation after diamide stress (C719) PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- UniProt: P80877
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number: 2.1.1.14
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Operon: metE
- Regulatory mechanism: S-box: transcription termination/ antitermination, the S-box riboswitch binds S-adenosylmethionine resulting in termination PubMed
- Additional information: subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Ana Gutiérrez-Preciado, Tina M Henkin, Frank J Grundy, Charles Yanofsky, Enrique Merino
Biochemical features and functional implications of the RNA-based T-box regulatory mechanism.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2009, 73(1);36-61
[PubMed:19258532]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jerneja Tomsic, Brooke A McDaniel, Frank J Grundy, Tina M Henkin
Natural variability in S-adenosylmethionine (SAM)-dependent riboswitches: S-box elements in bacillus subtilis exhibit differential sensitivity to SAM In vivo and in vitro.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(3);823-33
[PubMed:18039762]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Christine Eymann, Dörte Becher, Jörg Bernhardt, Katrin Gronau, Anja Klutzny, Michael Hecker
Dynamics of protein phosphorylation on Ser/Thr/Tyr in Bacillus subtilis.
Proteomics: 2007, 7(19);3509-26
[PubMed:17726680]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Falko Hochgräfe, Jörg Mostertz, Dierk-Christoph Pöther, Dörte Becher, John D Helmann, Michael Hecker
S-cysteinylation is a general mechanism for thiol protection of Bacillus subtilis proteins after oxidative stress.
J Biol Chem: 2007, 282(36);25981-5
[PubMed:17611193]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Falko Hochgräfe, Jörg Mostertz, Dirk Albrecht, Michael Hecker
Fluorescence thiol modification assay: oxidatively modified proteins in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2005, 58(2);409-25
[PubMed:16194229]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ulrike Mäder, Georg Homuth, Christian Scharf, Knut Büttner, Rüdiger Bode, Michael Hecker
Transcriptome and proteome analysis of Bacillus subtilis gene expression modulated by amino acid availability.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(15);4288-95
[PubMed:12107147]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
F J Grundy, T M Henkin
The S box regulon: a new global transcription termination control system for methionine and cysteine biosynthesis genes in gram-positive bacteria.
Mol Microbiol: 1998, 30(4);737-49
[PubMed:10094622]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)