Difference between revisions of "PdhA"
(→Expression and regulation) |
(→References) |
||
| Line 128: | Line 128: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | + | ==Reviews== | |
| + | <pubmed> 19476487 9655937 2227213 6805383 </pubmed> | ||
| + | ==Original publications== | ||
<pubmed>9352926,,12850135 6414463 11976308 20081037 </pubmed> | <pubmed>9352926,,12850135 6414463 11976308 20081037 </pubmed> | ||
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 19:17, 19 January 2010
- Description: pyruvate dehydrogenase (E1 alpha subunit)
| Gene name | pdhA |
| Synonyms | aceA |
| Essential | yes |
| Product | pyruvate dehydrogenase (E1 alpha subunit) |
| Function | links glycolysis and TCA cycle |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Central C-metabolism | |
| MW, pI | 41 kDa, 5.837 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1113 bp, 371 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ykyA, pdhB |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 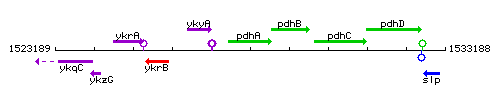
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU14580
Phenotypes of a mutant
- pdhA is essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Pyruvate + [dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase] lipoyllysine = [dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase] S-acetyldihydrolipoyllysine + CO2 (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information: Michaelis-Menten PubMed
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Inhibited thiamine 2-thiothiazolone diphosphate and NADH PubMed
- Low sensibility to NADPH
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure: 1W88 (E1 in complex with subunit binding domain of E2, Geobacillus stearothermophilus)
- UniProt: P21881
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 1.2.4.1
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- stringent response: due to presence of guanine at +1 position of the transcript PubMed
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Arthur Aronson, Purdue University, West Lafayette, USA homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
Shigeo Tojo, Kanako Kumamoto, Kazutake Hirooka, Yasutaro Fujita
Heavy involvement of stringent transcription control depending on the adenine or guanine species of the transcription initiation site in glucose and pyruvate metabolism in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2010, 192(6);1573-85
[PubMed:20081037]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hans-Matti Blencke, Georg Homuth, Holger Ludwig, Ulrike Mäder, Michael Hecker, Jörg Stülke
Transcriptional profiling of gene expression in response to glucose in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the central metabolic pathways.
Metab Eng: 2003, 5(2);133-49
[PubMed:12850135]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Haichun Gao, Xin Jiang, Kit Pogliano, Arthur I Aronson
The E1beta and E2 subunits of the Bacillus subtilis pyruvate dehydrogenase complex are involved in regulation of sporulation.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(10);2780-8
[PubMed:11976308]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M M Nakano, Y P Dailly, P Zuber, D P Clark
Characterization of anaerobic fermentative growth of Bacillus subtilis: identification of fermentation end products and genes required for growth.
J Bacteriol: 1997, 179(21);6749-55
[PubMed:9352926]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
P N Lowe, J A Hodgson, R N Perham
Dual role of a single multienzyme complex in the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate and branched-chain 2-oxo acids in Bacillus subtilis.
Biochem J: 1983, 215(1);133-40
[PubMed:6414463]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)