Difference between revisions of "NrdE"
(→Expression and regulation) |
|||
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
=Expression and regulation= | =Expression and regulation= | ||
| − | * '''Operon:''' ''[[nrdI]]-[[nrdE]]-[[nrdF]]-[[ymaB]]'' | + | * '''Operon:''' ''[[nrdI]]-[[nrdE]]-[[nrdF]]-[[ymaB]]'' {{PubMed|16885274}} |
| − | * '''[[Sigma factor]]:''' | + | * '''[[Sigma factor]]:''' [[SigA]] {{PubMed|16885274}} |
| − | * '''Regulation:''' | + | * '''Regulation:''' |
| − | ** expressed under anaerobic conditions ([[ResD]]) | + | ** expressed under anaerobic conditions ([[ResD]]) {{PubMed|16885274}} |
| − | * '''Regulatory mechanism:''' | + | * '''Regulatory mechanism:''' |
| − | ** [[ResD]]: transcription activation | + | ** [[ResD]]: transcription activation {{PubMed|16885274}} |
* '''Additional information:''' subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=+17981983 PubMed] | * '''Additional information:''' subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=+17981983 PubMed] | ||
Revision as of 20:17, 16 October 2009
- Description: ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase (major subunit)
| Gene name | nrdE |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase (major subunit) |
| Function | synthesis of deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Purine salvage, Nucleotides (regulation) | |
| MW, pI | 80 kDa, 5.931 |
| Gene length, protein length | 2100 bp, 700 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | nrdI, nrdF |
| Gene sequence (+200bp) | Protein sequence |
Genetic context 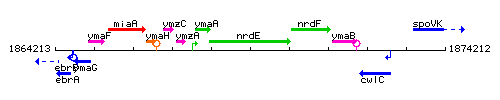
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU17380
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: 2'-deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate + thioredoxin disulfide + H2O = ribonucleoside diphosphate + thioredoxin (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase large chain family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): YosN
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P50620
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Additional information: subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Elisabeth Härtig, Braunschweig, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References